Nitrogen-fixing bacteria which convert atmospheric nitrogen to nitrates. The nitrogen cycle is a biogeochemical process in which nitrogen in various forms is circulated from the atmosphere to the living organisms and later back to the atmosphere.
Most nitrogen is found in the air as a gas.
. Log in Sign up. These bacteria are anaerobic and live in swampy soil or deep down in the soil where water accumulates. Clostridium free-living in the soil and.
2 Nitrogen fixation in the soil. Nitrogen fixation 14 Terms. When animals eat the plants they acquire usable nitrogen compounds.
During assimilation or when plants take up nitrates from the soil bacteria aid in the process with the plants in making ammonia. The nitrogen cycle refers to the cycle of nitrogen atoms through the living and non-living systems of Earth. Nitrogen is found in different forms in the earths surface.
Living organisms require nitrogen for the synthesis of nucleic acid and proteins. The nitrogen cycle can be broken down into four types of. Nitrogen atoms are found in all proteins and.
Some stages of the nitrogen cycle where bacteria have a high significance are. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Nitrogen is unreactive so it cannot be used directly by plants to make protein.
The importance of the nitrogen cycle are as follows. Most plants obtain nitrogen in the form of nitrates from the soil and use them to produce proteins. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
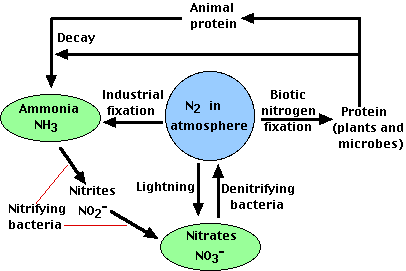
Nitrogen fixation nitrification assimilation and denitrification. Denitrification is the process through which the nitrates and nitrites are converted back to atmospheric nitrogen. In the nitrogen fixation process nitrogen fixing bacteria converts the N 2 in the atmosphere into N H 3 ammonia.
Name 2 bacteria that are nitrogen fixers. The conversion of nitrates to nitrogen gas. It is a continuous cycle maintained by the decomposers and other bacteria.
Another example is cyanobacteria. The atmosphere contains almost 78 of nitrogen present in an inert form N2. Legume plants such as peas beans and clover contain nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
Plants must secure their nitrogen. N 2 gas is a very stable compound due to the strength of the triple bond between the nitrogen atoms. The plants need the nitrogen for the synthesis of proteins and other compounds.
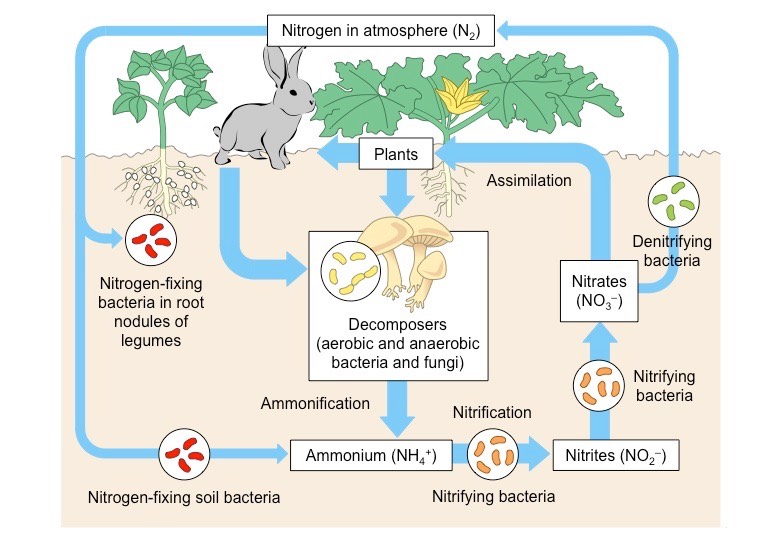
The nitrogen cycle illustrates how nitrogen flows in the environment between plant animals bacteria soil water and the atmosphere. Nitrogen is essential for the formation of amino acids in proteins or for use in necessary biomolecules such a nucleic acids. The Nitrogen cycle is the biochemical cycle which involves bacteria.
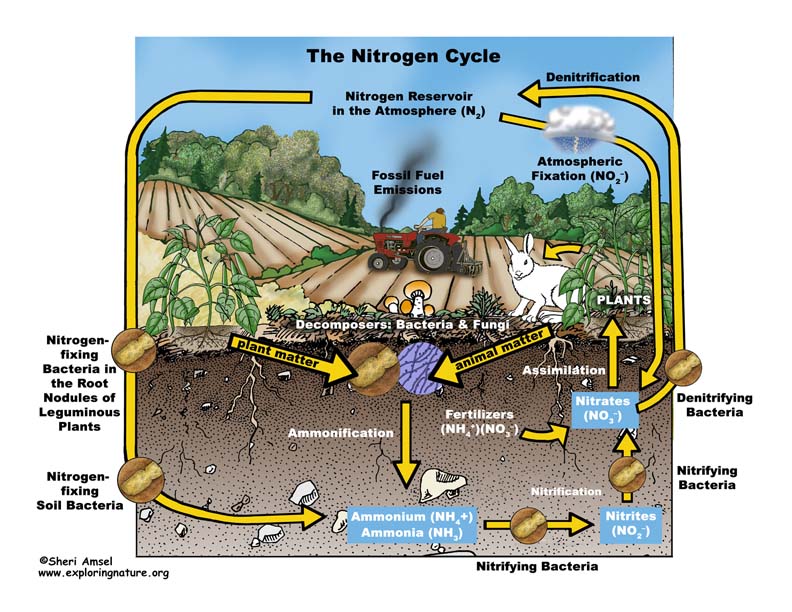
The nitrogen cycle is the movement of nitrogen between the earth and the atmosphere. Waste products undigested food urine and faeces and dead organisms. 78 of the earth atmosphere contains Nitrogen gas.
The stages of the nitrogen cycle. Start studying Bacteria Role in Nitrogen Cycle. The nitrogen cycle explains the how nitrogen flows between animals bacteria plants the atmosphere and the soil on earth.
Helps in converting inert nitrogen gas into a usable form for the plants through the biochemical process. Bacteria - Nitrogen Cycle Lecture 10. The nitrogen compounds are passed through the food chain as other organisms feed on the plants and each other.
It consists of a series of processes that convert nitrogen gas to organic substances and these back to nitrogen in nature. The Nitrogen fixing bacteria are either free living or symbiotic. Helps plants to synthesise chlorophyll from the nitrogen compounds.
Animals obtain nitrogen as. The nitrogen cycle would stop and ecosystems would collapse. Nitrogen is a key component of the bodies of living organisms.
The nitrogen cycle is vital for life on Earth. The uniqueness of the nitrogen cycle is that nitrogen is the most abundant gas in the earths atmosphere about 78 of all air but it cant be directly utilized by the animals and plants unless it is converted into. Bacteria play a central role.
Cycle Packet QA 24 Terms. It is carried out by denitrifying bacteria in the soil. The process of converting N 2 into biologically available nitrogen is called nitrogen fixation.
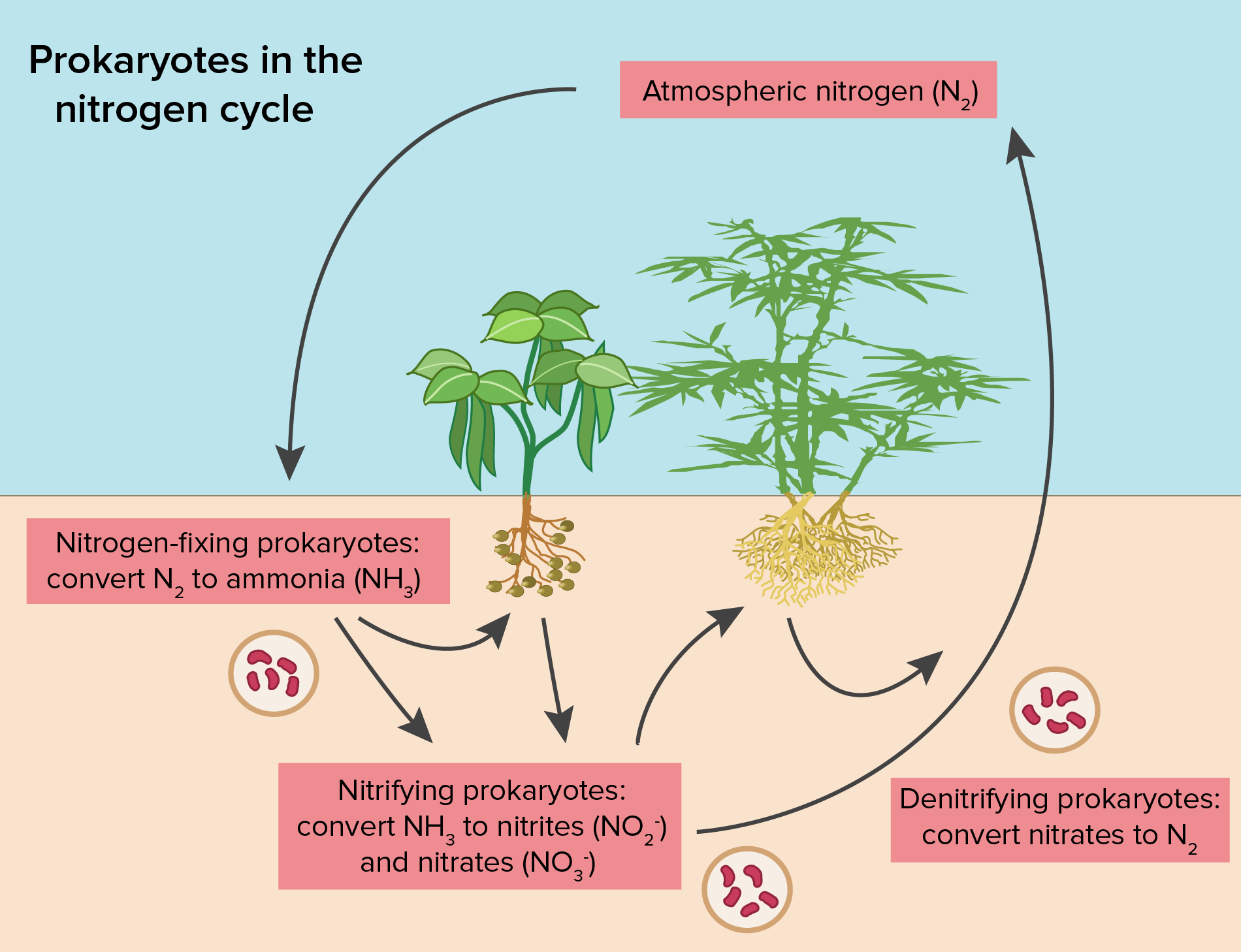
Nitrogen fixing bacteria reside in the root nodules of leguminous plants where they fix atmospheric nitrogen into forms of nitrogen usable by the plant. This process is performed by the anaerobic bacteria. And involves the atmosphere hydrosphere and lithosphere.
In nitrogen fixation bacteria convert into ammonia a form of nitrogen usable by plants. Nitrogen Cycle and Carbon Cycle 12 Terms. Plants absorb the nitrate ions by diffusion and active transport.
Only nitrates are useful to plants so other processes are needed to convert free nitrogen N 2 to useable forms. These bacteria live in swellings in the plant roots called. Start studying Bacteria - Nitrogen Cycle Lecture 10.
Bacteria plays a vital role in the conversion of free nitrogen into biologically available forms. Bacteria help in nitrogen fixation either as free-living entities or through symbiotic relationships with animals and plants such as legumes. This bacteria binds hydrogen molecules with the gaseous nitrogen to form ammonia in the soil.
Role of organisms in the nitrogen cycle. In the process of ammonification the bacteria help in decomposing the animal and plant. Importance of Nitrogen Cycle.
1 Nitrogen fixing in the root nodules of legumes. In nitrification a host of soil bacteria participate in turning ammonia. The nitrogen cycle is the recycling phase of the nitrogen which includes nitrogen fixation ammonification nitrification and denitrification.
Nitrogen exists in the atmosphere as gas. The nitrogen cycle involves four major steps. 78 of the air is nitrogen.
Through the cycle atmospheric nitrogen is converted to a form which plants can incorporate into new proteins. Nitrogen Cycle WebQuest 18 Terms.
17 2b Nitrogen Cycle Biology Libretexts
How Would You Explain The Nitrogen Cycle Socratic
What Are The Roles Of Bacteria In The Nitrogen Cycle Socratic
0 Comments